Today we shall continue discussing functions in C++. You can check out parts one, two and three.
References and Reference Parameters
•
Call by value
–
Copy of data passed to function
–
Changes to copy do not change original
–
Prevent unwanted side effects
•
Call by reference
–
Called Function can directly access data of
calling function
–
Changes affect original
•
Reference parameter
–
Alias for argument in function call
•
Passes parameter by reference
–
Use & after data type in prototype
•
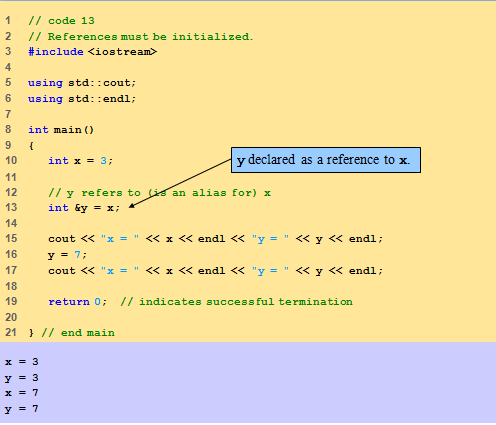
void myFunction( int &data )
•
Read “data is a reference to an int”
–
Function call format the same
•
However, original can now be changed
•
Pointers
–
Another way to pass-by-reference
•
References as aliases to other variables
–
Refer to some variable and only one variable
•
References must be initialized when declared
–
Otherwise, compiler error
Default Arguments
•Function call with omitted
parameters
–If not enough
parameters, rightmost go to their defaults
–Default values
•Can be global
variables, constants, expressions or function calls
•Set defaults in function
prototype
int myFunction( int x = 1, int y = 2, int z = 3 );
–myFunction(3)
•x = 3, y and z get defaults
(rightmost)
–myFunction(3, 5)
•x = 3, y = 5 and z gets default
Unitary Scope Resolution Operator
•Unary scope resolution operator (::)
–Access global
variable if local variable has same name
–Not needed if
names are different
–Use ::variable
•y = ::x + 3;
–Good to avoid
using same names for locals and globals













Post a Comment