Continuing with the previous post, today we will further go into details about functions.
Attributes of a Variable:
All variables have attribute,which include;
Functions with Empty Parameter Rules:
Inline Functions:
Attributes of a Variable:
All variables have attribute,which include;
and;
–Scope
•Where
variable can be referenced in program
–Storage
class
•How
long variable exists in memory
Storage Classes:
Thee are two storage classes:
–Automatic
–Static
Automatic Storage Classes:
Automatic storage class are either auto or register
–Variable
created when program enters block in which it is defined
–Variable
destroyed when program leaves block
–Local
variables of functions are automatic
•Automatic
by default
•keyword
auto
explicitly
declares automatic
–register
keyword
•Hint
to place variable in high-speed register
•Good
for often-used items (loop counters)
•Often
unnecessary, compiler optimizes on its own
–Specify
either register
or auto,
not both
•register int counter = 1;
Static Storage Classes:
In static
storage class;
–Variables
exist for entire program
•For
functions, name exists for entire program
–Not
accessible outside one file, scope rules still apply
•static
keyword
–Local
variables
–Keeps
value between function calls
–Only
known in own function
•extern
keyword
–Default
for global variables/functions
•Globals:
defined outside of a function block
–Known
in any function that comes after it
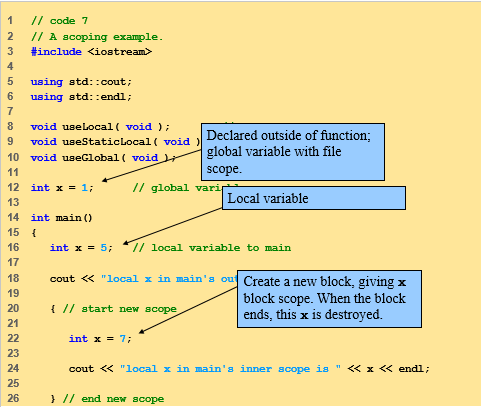
Scope Rules:
Scope is the portion
of program where identifier can be used, it has further four categories
•File
scope aka Global scope
–Defined
outside a function, known in all functions
–Global
variables, function definitions and prototypes
•Function
scope
–Labels
are the only identifiers with function scope
–Can
only be referenced inside defining function
–Only
labels, e.g., identifiers with a colon (case:)
–Labels
used with ‘goto’
statement
•Block
scope/Local scope
–Begins
at declaration, ends at right brace }
•Can
only be referenced in this range
–Local
variables, function parameters
–static
variables still have block scope
•Storage
class separate from scope
•Function-prototype
scope
–Parameter
list of prototype
–Names
in prototype optional
•Compiler
ignores
–In
a single prototype, name can be used only once
In c++ we often encounter functions with Empty
parameter lists;
–void or
leave parameter list empty
–Indicates
function takes no arguments
–Function
print
takes no arguments and returns no value
•void print();
•void print( void );
Inline
functions are a very useful in programming, if we know where to use them;
–Keyword
inline
before function
–Asks
the compiler to copy code into program instead of making function call
•Reduce
function-call overhead
•Compiler
can ignore inline
–Good
for small, often-used functions
•Example
inline
double cube( const
double s )
{
return s * s * s; }
–const
tells compiler that function does not modify s
















Post a Comment