Previously we completed the concept of Arrays (parts one, two three and four), today we will discuss the basics of Pointers.
Pointer Variable Declarations and Initialization
• Pointer variables:
– Contain memory addresses as values
– Normally, variable contains specific value
(direct reference)
– Pointers contain address of variable that has
specific value (indirect reference)
•
Indirection
– Referencing value through pointer
•
Pointer declarations
– *
indicates variable is pointer
int *myPtr;
declares pointer to int, pointer of type int *
– Multiple pointers require multiple asterisks
int *myPtr1, *myPtr2;
• Can declare pointers to any data type
• Pointer initialization
– Initialized to 0, NULL, or address
•
0 or NULL points to nothing, and is
called ‘Null Pointer’
Pointer Operators:
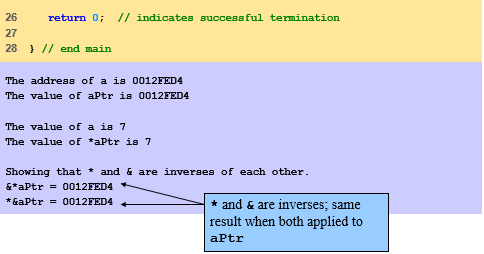
•&
(address operator)
–Returns
memory address of its operand
–Example
int y = 5;
int *yPtr;
yPtr = &y; // yPtr gets address of y
int *yPtr;
yPtr = &y; // yPtr gets address of y
–yPtr
“points to” y
•*
(indirection/dereferencing operator)
–*yPtr
returns y
(because yPtr
points to y).
*yptr = 9; // assigns 9 to y
cout<<*yptr;
cin>>*yptr;
•* and & are
inverses of each other
Calling Functions by Reference
•
3 ways to pass arguments to function
–
Pass-by-value
–
Pass-by-reference with reference arguments
–
Pass-by-reference with pointer arguments
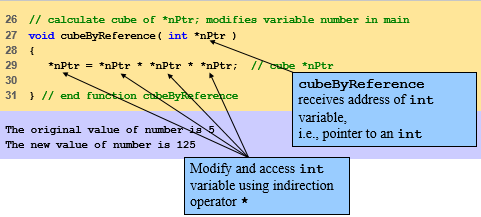
•
Pass-by-reference with pointer arguments
–
Use pointers and indirection/dereferencing
operator
–
Pass address of argument using &
operator
–
* operator used as alias/nickname for
variable inside of function










Post a Comment